Dementia Research Entering Exciting New Phase Focusing On Early Detection, Brain Health Clinics And New Drugs
Dementia may become treatable in the years ahead if detected early like breast cancer as researchers make real progress on the latest disease modifying drugs, biomarker screening techniques and personalised risk plans.
Professor Craig Ritchie, a world-leading authority on dementia and an investigator on more than 30 drug trials, told HammondCare’s International Dementia Conference 2020 today that dementia and neurodegenerative disease research and care are undergoing a paradigm shift.
Professor Ritchie said he expected a future where networks of brain health clinics like those being developed by Brain Health Scotland, which launched this month, would play a central role in early detection, individualised risk reduction and ongoing disease management.
“There is good evidence emerging that the diseases we know in later life as dementia, or late stage neurodegenerative disease, are really evident from mid life onwards,” Prof. Ritchie said.
He likened the period of mid life among people likely to develop dementia later as a “silent period” for brain disease. “But it’s only silent because we are not listening,” he said.
“My argument is its time to really start focussing our attention on detection in these populations as early as possible and this is the best chance of impacting on the course of the disease.”
Early detection of dementia, or neurodegenerative disease, could become like breast cancer where mammograms can detect pre-cancerous or early tumours and at that point the disease can be effectively managed with the best treatments.
Prof Ritchie’s keynote address to the IDC 2020 is based on a paper he produced, along with other researchers in the field, outlining the present promising state of research published in August 2020 edition of Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association.
The latest research suggests 40 per cent of the incidence of dementia is due to 12 modifiable lifestyle risk factors — hypertension, obesity, smoking, physical activity, diabetes, social isolation, hearing loss, depression, low education, traumatic brain injury, excess alcohol consumption and air pollution.
People in mid life can reduce their chances of the disease by changing these lifestyle factors. The remainder of disease risk is probably attributable to a complex interplay between abnormal tau- and beta-amyloid proteins.
The next phase of treatment will be in emerging secondary prevention where individuals detected early through screening to be at high risk of cognitive impairment and dementia can benefit from emerging disease modifying anti-amyloid and anti-tau drugs.
These treatments were most likely to be effective in the early stages of neurodegenerative disease. In 2019 there were six such disease modifying drugs undergoing phase III trials and their results are eagerly awaited.
One of them Aducanumab – administered by an infusion every four weeks – has been filed for fast-track review with the US Food and Drug Administration with a decision expected by March 2021. Another promising drug is Anavex 2-73, which has involved Australians in phase III trials.
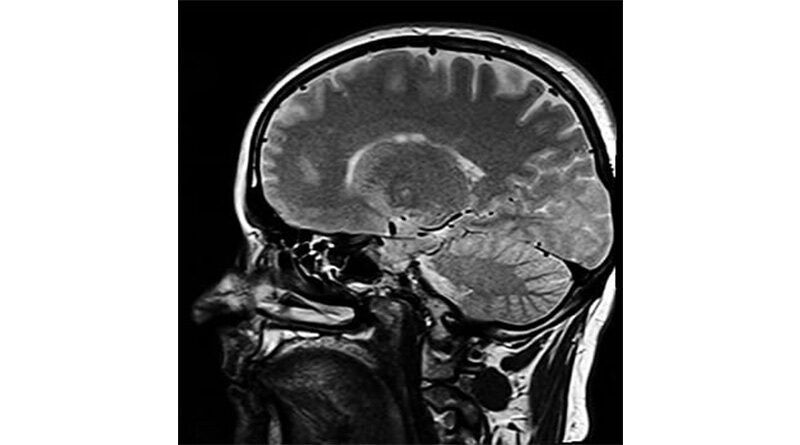
Professor Ritchie, Professor of Psychiatry of Ageing at the University of Edinburgh, said advances in blood-based biomarkers of amyloidosis, tauopathy and neurodegeneration open the door for reliable and effective screening and early treatment.
He said brain health service clinics, a development on today’s memory clinics, would help people with pre-clinical signs of neurodegenerative disease manage their brain health.
Another role for the brain health clinics would be to better help the estimated one third of patients with functional cognitive disorders other than dementia who get wrongly diagnosed with the disease.
They may live for 10 or 15 years believing they have dementia but experience no cognitive decline. “We are doing these people a massive disservice by giving them a false positive,” he said.
Early detection would have the added benefit of creating a growing group of people available for phase IV trials of new disease modifying treatments. Brain health clinics would play a key role in overseeing these trials with artificial intelligence ensuring the most effective collection of trial data.